alpha Zearalenol
Details
Specifications
Chemical identification
Synonyms:
- Alpha-Zearalenol;
- Trans-Zearalenol,
- α-Zearalenol;
- a-Zearalenol
Chemical names:
- Alpha-Zearalenol;
IUPAC:
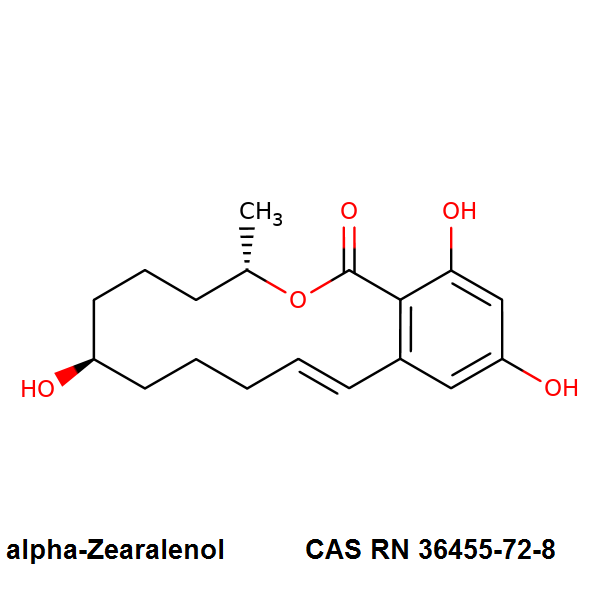
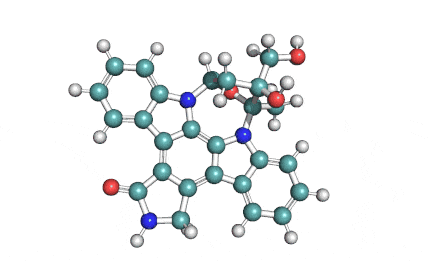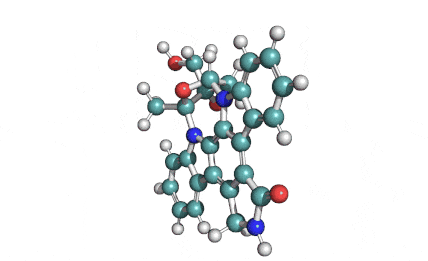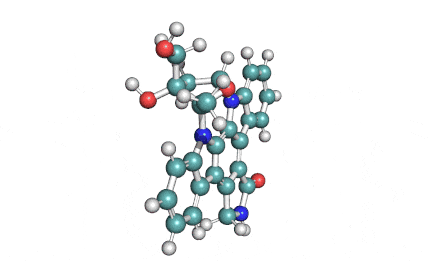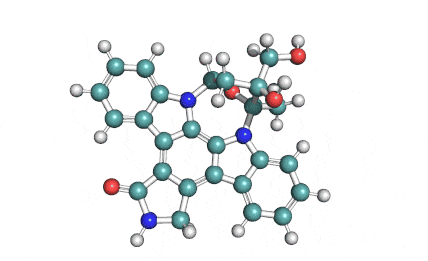
(3S,7R,11E)-7,14,16-Trihydroxy-3-methyl-3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10-octahydro-1H-2-benzoxacyclotetradecin-1-one
RTECS# DM2560000
Alpha-Zearalenol is a synthetic derivative of the macrolactone mycotoxin zearalenone, which is also manufactured by Fermentek by the method of fungal fermentation.. Alpha-Zearalenol is estrogenically active and demonstrates induction of premature uterine growth, increase of nuclear estrogen receptor levels, and a five fold increase of ornithine decarboxylase level (ODC). The increase of ODC level was 20-fold more pronounced with Alpha-Zearalenol than zearalenone, and Alpha-Zearalenol demonstrated three times more potent estrogenic activity than zearalenone.
Further Information
Composition
Special Info
Other Fields