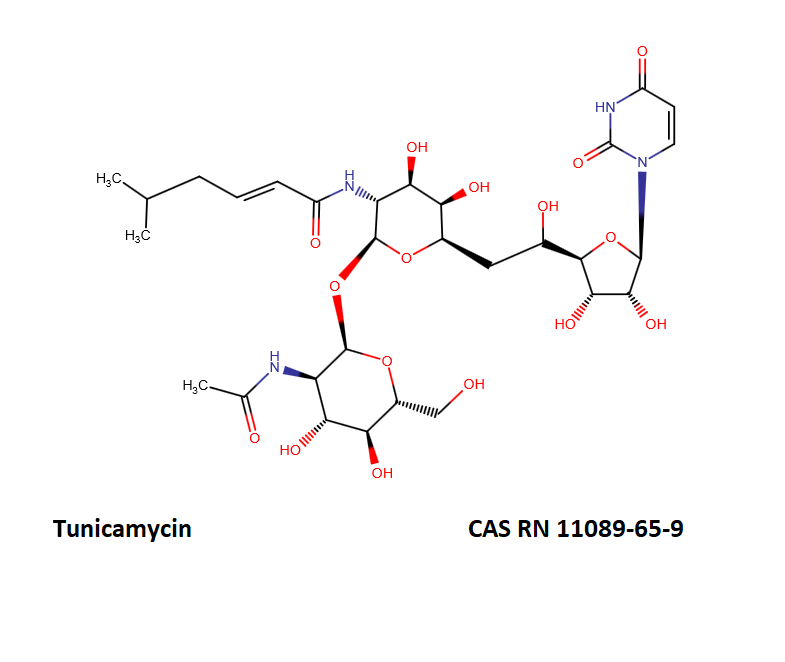
Tunicamycin (complex)
Details
Specifications
Clear colorless to brown solution at 50mg/ml of DMSO
Chemical identification
RTECS: YO7980200
Tunicamycin is a mixture of homologous nucleoside antibiotics.
The main homologs differ in the length of the fatty chain moiety.
The following table defines the four main Tunicamycin homologs.
- Tunicamycin A, aka Tunicamycin V, n=9, mw=817;
- Tunicamycin B, aka Tunicamycin VII, n=10, mw=831;
- Tunicamycin C, aka Tunicamycin II, n=8, mw=845;
- Tunicamycin D, aka Tunicamycin X, n=11, mw=859
Further Information
- Tunicamycin is soluble in DMSO, alkaline water, hot methanol.
- Practically insoluble in acetone, ethyl acetate.
- Unstable in acidic solutions
- nucleoside antibiotic
- antiviral
- inhibitor of glucosylation of proteins
- tunicamycin causes cell cycle arrest in G1 phase
- Tunicamycin has anti-angiogenesis properties.
Tunicamycins inhibit protein glycosylation. They arrest cell cycle in late G1As Tunicamycin affects cell membrane permeability, it was shown to increase production of antibiotics, such as streptomycin PRODUCT USE A tool to study glycoprotein synthesis in a wide variety of biological systems. Family of nucleoside antibiotics produced by Streptomyces lysosuperificus. Tunicamycin interferes with glycoprotein synthesis in yeast and mammalian systems and enhances antiviral and anticellular activity of interferon. Possesses cell - surface altering activity. Inhibits the transfer of N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate from UDP -N- acetylglucosamine to dolichol monophosphate and thereby blocks the formation of N-glycosidic protein-carbohydrate linkages. Active in vitro against Gram-positive bacteria, yeasts, fungi and viruses.
Composition
Special Info
Other Fields