Details
Specifications
Chemical identification
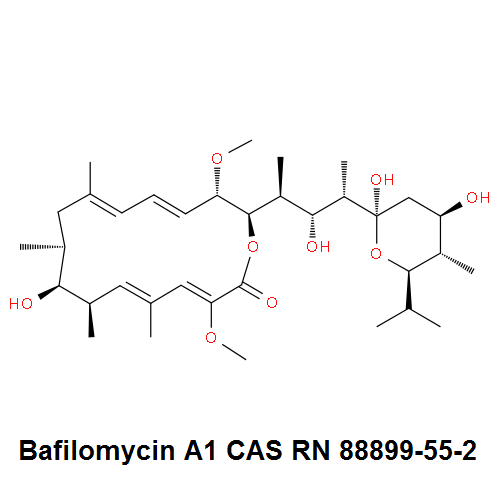
IUPAC Name: (3Z,5E,7R,8S,9S,11E,13E,15S,16R)-8-Hydroxy-16-[(1S,2R,3S)-2-hydroxy-1-methyl-3-[(2R,4R,5S,6R)-tetrahydro-2,4-dihydroxy-5-methyl-6-(1-methylethyl)-2H-pyran-2-yl]butyl]-3,15-dimethoxy-5,7,9,11-tetramethyloxacyclohexadeca-3,5,11,13-tetraen-2-one
Bafilomycin A1 is toxic macrolide antibiotic acts as a specific inhibitor of vacuolar-type H+-ATPase. It acts as autophagy Inhibitor
Further Information
Soluble in 100% ethanol, methanol or DMSO.
Macrolide antibiotic
Bafilomycin A1 is a specific inhibitor of vacuolar type H+-ATPase (V-ATPase) in animal cells, plant cells and microorganisms. Bafilomycin A1 is useful in distinguishing among different types of ATPases. Bafilomycin A1 can prevent the re-acidification of synaptic vesicles once they have undergone exocytosis. Antibacterial, Antifungal, Antineoplastic, Immunosuppressive Bafilomycin A1 has been shown to decrease multi-drug resistance.
Bafilomycin A1, inhibits vacuolar-ATPase.
It is a potassium ionophore that impairs mitochondrial functions.
It activates respiration of neuronal cells via uncoupling associated with flickering depolarization of mitochondria.
Bafilomycin A1 has been commonly used as a method of inhibition of infection by viruses known or suspected to follow the path of receptor-mediated endocytosis and low-pH-mediated membrane fusion
Vacuolar ATPase inhibitors overcome Bcl-xL-mediated chemoresistance through restoration of a caspase-independent apoptotic pathway.
Composition
Special Info
Other Fields