Details
Specifications
Chemical identification
Synonyms
- Cerulenin
- Helicocerin
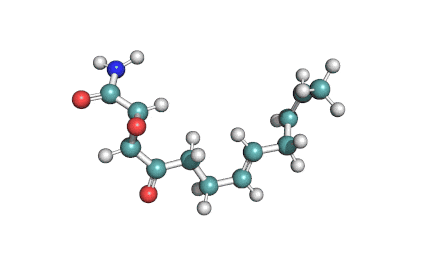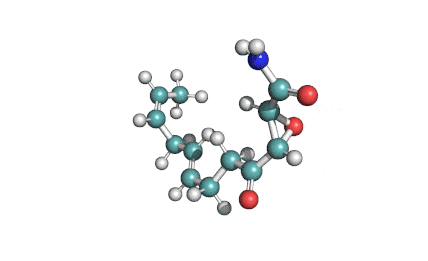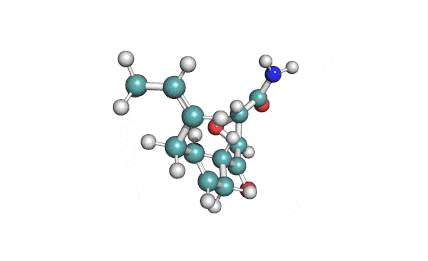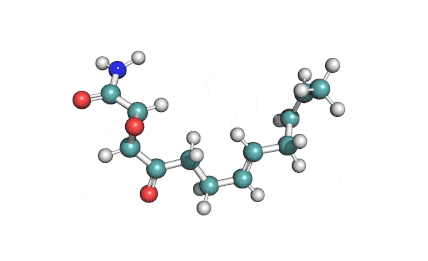
IUPAC Name: (2R,3S)-3-[(4E,7E)-Nona-4,7-dienoyl]oxirane-2-carboxamide
Systematic name: (2R,3S)-3-[(4E,7E)-4,7-Nonadienoyl]-2-oxiranecarboxamide
RTECS: JR1670000
Cerulenin: an antifungal antibiotic, fatty acids and sterols biosynthesis inhibitor.
Further Information
Cerulenin is soluble in DMSO, Methanol, Ethanol, Dichloromethane, Acetone, Benzene and most common solvents. Concentrations up to 20 mg/ml can be achieved. Slightly soluble in H2O. Concentrations up to 0.2 mg/ml are achievable.Not soluble in Petrol Ether.Attention: Cerulenin is unstable in aqueous solutions, and very unstable in basic solutions
- Fatty acid antibiotic.
- Apoptosis inducer
- Antifungal antibiotic
- Mycobacteria inhibitor
Cerulenin was originally proposed as antifungal antibiotic. Cerulenin is used as a biochemical tool. Cerulenin has been shown to cause dramatic weight loss in animals. Cerulenin blocks synthesis of fatty acids and sterols by binding to the enzyme fatty-acid-synthase. In some tumor lines, this triggers apoptosis., an effect believed to be mediated by the accumulation of malonyl-coenzyme A in cells with an upregulated FAS pathway.
Composition
Special Info
Other Fields