Details
Specifications
Chemical identification
Synonyms:
- Isocercosporin
- Cercosporin
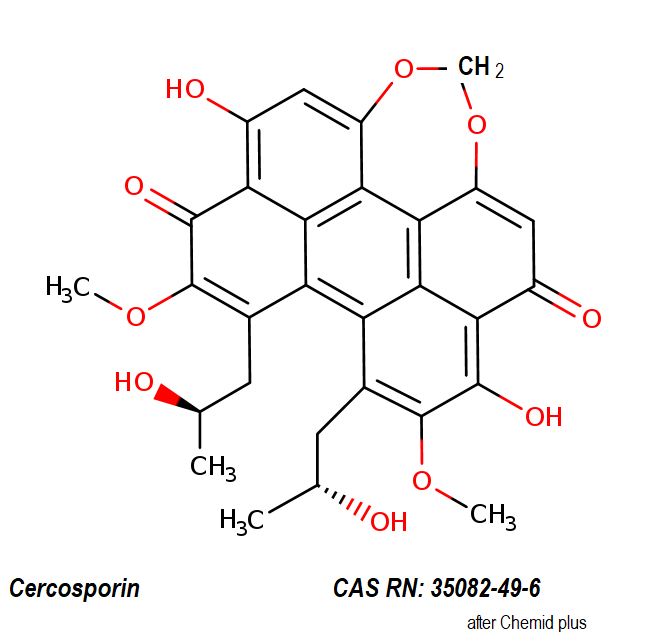
IUPAC: 5,12-Dihydroxy-8,9-bis[(2R)-2-hydroxypropyl]-7,10-dimethoxyperylo[1,12-def][1,3]dioxepine-6,11-dione
Chemical names:
RTECS#: N.A.
Cercosporin is a light-induced polyketide phytotoxin reported to produce singlet oxygen when photoactivated. Acts as a potent and specific PKC inhibitor. Competes for the phorbol binding site. Anticancer compound. Also displays antiproliferative; antiparasitic and antimicrobial properties. Cercosporin is a photosensitizing toxin produced by fungal plant pathogens in the genus Cercospora. Cercosporin produces singlet oxygen and superoxide when irradiated by light, and damages plants by causing a peroxidation of the membrane lipids. This membrane damage leads to a loss in membrane fluidity, leakage of nutrients, and rapid death of the plant cell. Cercosporin is toxic to mice and bacteria in addition to plants, and attempts to select plant cells in vitro for resistance to cercosporin have not been successful. A large number of fungal species, however, are resistant to cercosporin. Carotenoids and the fungal cell wall appear to play a critical role in the resistance of fungi to cercosporin.
Further Information
- Soluble in DMSO, ethanol or methanol (lit)
- Soluble in 1mg/ml ethanol, methanol, DMSO
- Soluble in 1mg/liter H2O
- Melting Point: 241℃ lit - Scifinder
- Anticancer agent
- protein kinase C inhibitor
Composition
Supply related information
Special Info
Other Fields





![Mitomycin C [1mg Mitomycin C + 24mg NaCl] Mitomycin C [1mg Mitomycin C + 24mg NaCl]](/sites/default/files/2024-02/Mitomycin-C%20NaCL%20Mix.png)