Details
Specifications
Clear yellow solution at 5mg/ml DMSO ;
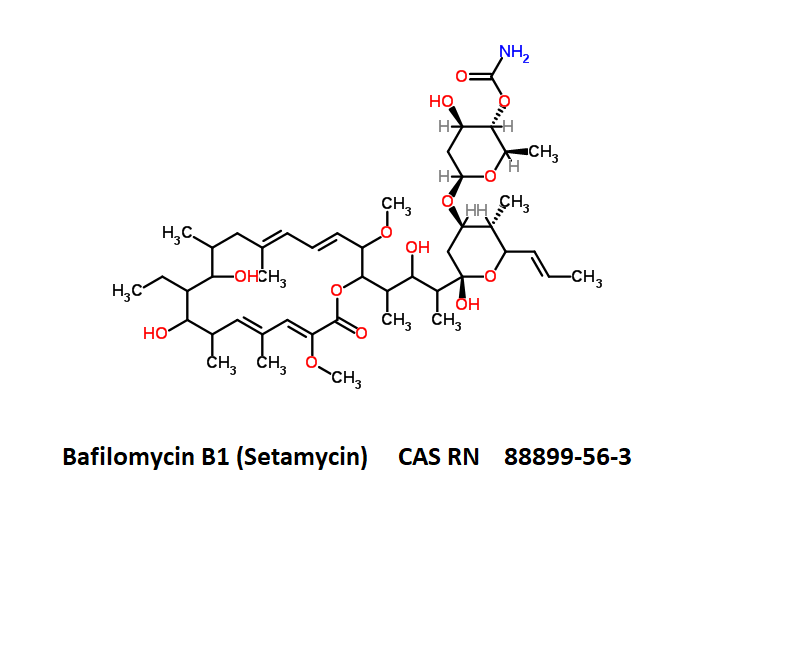
Chemical identification
Synonyms
- Hygrolidin, 37-decarboxy-2-demethyl-37-[[(2-hydroxy-5-oxo-1-cyclopenten-1-yl)amino]carbonyl]-2-methoxy-24-methyl
- Setamycin
- Bafilomycin B1
IUPAC Name
- (5R)-2,4-Dideoxy-1-C-{(2S,3R,4S)-3-hydroxy-4-[(3S,4Z,9S,10S,11R)-10-hydroxy-3,15-dimethoxy-7,9,11,13-tetramethyl-16-oxooxacyclohexadeca-4,6,12,14-tetraen-2-yl]-2-pentanyl}-3-O-{(2E)-4-[(2-hydroxy-5-ox ;o-1-cyclopenten-1-yl)amino]-4-oxo-2-butenoyl}-5-isopropyl-4-methyl-α-D-threo-pentopyranose
RTECS: NG8841000
Bafilomycin B1 is a specific inhibitor of vacuolar type H+-ATPase (V-ATPase) in animal cells, plant cells and microorganisms.
Bafilomycin B1 can prevent the re-acidification of synaptic vesicles once they have undergone exocytosis.
It displays Antibacterial, Antifungal, Antineoplastic, Immunosuppressive properties.
Bafilomycin B1 shares the same mode of action and activity as its more accessible Bafilomycin A1 analogue. Bafilomycin B1 is broadly active against bacteria, fungi, insects, nematodes and protozoans. Bafilomycin B1 has attracted interest as a potential antiosteoporotic agent in treating bone lytic diseases.
Bafilomycins have been considered as possible therapeutic agents in the treatment of gastritis.
Further Information
Reportedly soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF or DMSO. Attention: may form methyl ketal on long term storage in methanol
Macrolide antibiotic
Bafilomycins specificly inhibit vacuolar type H+-ATPase (V-ATPase) in animal cells, plant cells and microorganisms. Bafilomycin A1 is useful in distinguishing among different types of ATPases. Bafilomycin A1 can prevent the re-acidification of synaptic vesicles once they have undergone exocytosis. Bafilomycin A1 and B1 significantly attenuate cerebellar granule neuron death resulting from agents that disrupt lysosome. As vacuolar ATPase inhibitors bafilomycins overcome Bcl-xL-mediated chemoresistance through restoration of a caspase-independent apoptotic pathway.
Composition
Special Info
Other Fields