Beauvericin
Details
Specifications
Chemical identification
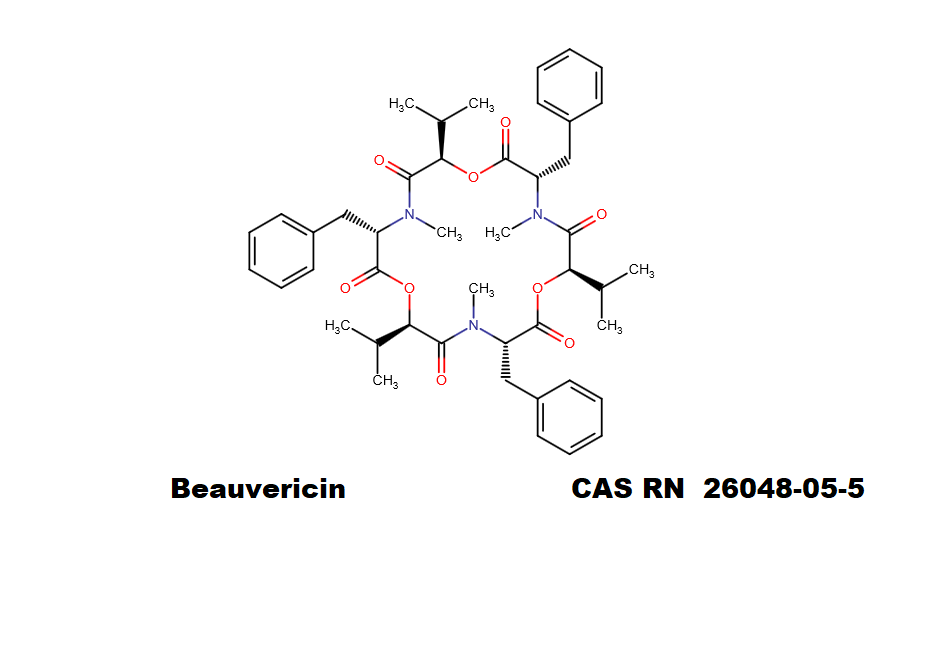
Beauvericin is a mycotoxin derived from the mould Beauveria bassiana, Fusarium strains and other moulds. Beauvericin belongs to the enniatin family of antibiotics. Beauvericin is a cyclic hexadepsipeptide with alternating L-N-methylphenylalanyl and D-a-hydroxyisovaleryl residues. While being toxic to insects, it is quite harmless for humans.
Further Information
Beauvericin insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents
Oligopeptide, ionophore, antibiotic
Beauvericin is active against Gram+ bacteria, mycobacteria, insects, brine shrimp. Beauvericin shows cytotoxic, Immunosuppressant, and apoptotic activity. Beauvericin is the most potent specific inhibitor of cholesterol acyltransferase and possesses ionophoric properties. Beauvericin increases ion permeability in biological membranes by forming a complex with essential cations (Ca2+, Na+, K+), which may affect the ionic homeostasis.
Composition
Special Info
Other Fields